Globally, the discourse on whether muscle can burn fat or not has remained for a very long time. However, several opinions have been stated by different health researchers and fitness specialists. To understand the whole concept of muscle burning fat or its capability to increase metabolism, it is salient that we have a basic understanding of muscles, metabolism, and the relationship between the two phenomena.
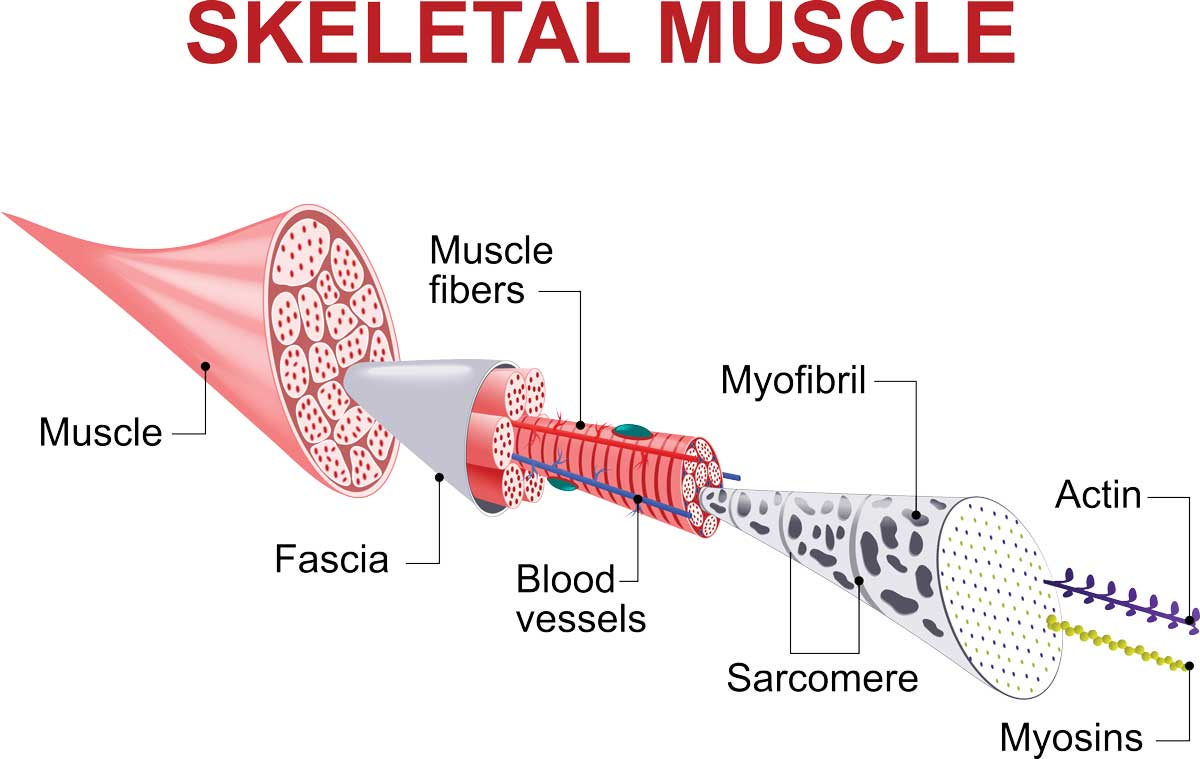
First off, most animals are created with muscles, which contains protein filaments of actin and myosin. These two filaments contract over one another to change the length and the shape of the muscle cells. Consequently, they can produce force and motion, including the contraction of the heart and digestive systems. However, the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates within the body system predominantly powers the muscle.
Speaking of metabolism, it is the chemical reaction necessary for the sustenance of living cells within the body. But metabolism is in two categories: Anabolic process and catabolic process. Anabolism is the synthesis of compounds that are needed by the cells. An excellent example of the anabolic process is the building of muscle tissues from amino acids. As for the catabolism, it involves the breaking down of large molecules into small elements such as the breakdown of muscle protein to amino acids to be used for gluconeogenesis.
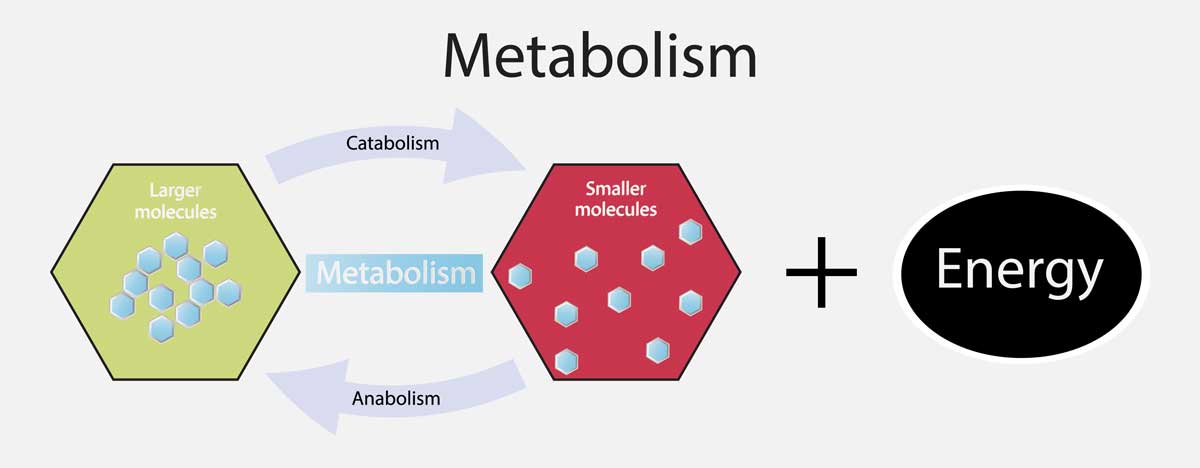
Therefore, we can say that the constant chemical reaction happening in the body and causing changes is called metabolism. Using the perspective of energy expenditure, metabolism is also referred to as the Resting Metabolic Rate, which is the amount of energy needed to maintain the core function of the body while at rest.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what muscles and metabolisms are. Let’s delve into the main question of whether muscle burns fat with a reasonable explanation. Kindly read to the end.
Does Muscle Burn Fat?
When it comes to whether muscles burn fat or not, a simple answer is that it does.
However, people have misconstrued the concept as they expect a significant result after a few weeks of hard and painful weightlifting, among other cardio exercises. Most people erroneously believe that the more muscle you gain, the higher will your metabolism ramps up and, consequently, helps burn off your fats. As a result, several people advocated for an intense weightlifting program for three to four weeks. But the truth is that it’s doesn’t work that way.
Truly, muscle building helps burn more calories and fat at rest. However, what’s not true is that one pound of muscle is capable of burning about 50 to 100 calories per day during the restive state. Research has shown that rather than 50 calories, one pound of muscle at rest can only burn around six calories per day. Therefore, even when you train hard and accrue about 10 pounds of muscles within five months, you would have consumed only 60 calories – which is not a whole lot to count on.
But this doesn’t mean that growing muscles won’t help burn down the calories – it could, as we have explained. The ability of a muscle to reduce your fats will depend on your body goals, diet and exercise engaged. If you focus on losing weight only, then a combination of exercise regime, most notably resistance training, and nutrition will help achieve a great result. And more so, sustaining the exercise level after reaching your desired body goal is as important as the routine itself.

For some people, the idea is to diet down, then bulk up to accrue lean muscle mass. Such people have to be mindful of their health. The reason is that people having more than 15% of body fat are likely to lose more fat than lean muscle while dieting, only to gain the fat back rather than gaining lean muscle mass. Ideally, slim people are expected to lose muscle mass whenever they want to reduce their body fat percentage, then gain lean muscle mass while putting on weight.
Thus, if you intend to reduce your body fat percentage and maintain it, you need to adhere to a maintenance diet for a couple of weeks after achieving your body goal. Also, it is salient that you continue with your weightlifting routine to regulate your hormones. So, for those who are already lean but would like to add muscle mass, the best advice is to bulk up until you reach 15%. Afterward, you should begin to work on reducing your body fat percentage again.
Always keep in mind that there is no shortcut to achieve a great body goal other than a healthy diet and regular exercise. With a healthy diet and lifestyle, you can start working on your muscles by doing some resistance training and a cardio routine. Again, it is worth noting that muscle does burn fat around it; however, it only burns in a small amount. You can only improve its effectiveness by combining a consistent muscle building with a healthy diet. Over time, your fat will reduce significantly, and you will gain an excellent shape that you have always wanted.
Does lifting weights increase metabolism?
Another crucial aspect of the discussion that worth considering is whether weightlifting helps speed up metabolism or not. To begin with, you should know that muscles alone don’t get to increase your resting metabolic rate significantly. According to research, working on your muscle growth, such as weightlifting, only increase the metabolism for some hours after an exercise.
Specifically, research has shown that heavy resistance training help raise the rate of oxygen consumption in young men for about 38 hours after an exercise. The rise in oxygen consumption is referred to as Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC). This change in oxygen consumption is an increased rate of oxygen intake after a rigorous activity that happens to cover for “oxygen deficit” in the body. During the recovery process, the human body will use EPOC to restore the body to a restive state, as well as adapts it to the just concluded exercise. Also, EPOC helps fuel the increased metabolism in the body as a result of the increased body temperature during the routine.
More importantly, EPCO occurs due to a rise in fat burning (lipid metabolism), glycogen re-synthesis, increased phosphagen, an increase in the rate of lactate removal, and an increased enabling of the sympathetic nervous system. The effect of EPOC is greatest immediately after the exercise is over, and with time, it will reduce to the barest minimum.
As our body tries to recover after lifting heavy weights, it will burn extra fat while the metabolism will increase. Knowing this point, several people often spend many hours running and engaging in cardio exercises. However, be informed that it will take 3,500 calories to burn a pound of fat. And if you run an entire one hour, you will only burn 500 calories, which means you will need to run six more hours to expend 3000 calories to shed off one pound – and that’s a lot to take.
Another crucial aspect of the discussion that worth considering is whether weightlifting helps speed up metabolism or not. To begin with, you should know that muscles alone don’t get to increase your resting metabolic rate significantly. According to research, working on your muscle growth, such as weightlifting, only increase the metabolism for some hours after an exercise..
For this reason, developing your muscles seems to be the most effective means of burning fat. By lifting weights to build your muscles, you get to burn fat during the process, and even after doing the routine compared to burning calories that only work for a few hours after an exercise. Considering that muscles weigh higher compared to fat, the human body tends to work more across the day, and consequently, burn more fat.
Also, you need to know the kind of exercises that help burn more fat. Compound exercises are recommendable because you get to work out multiple muscles at once. As a result, your body will experience metabolic shock, which will increase your metabolism. In this way, you will be burning more fat for several days. Beyond increasing the metabolic rate, weightlifting also helps regulate sugar level and improve blood pressure. Additionally, it is often recommended for improving gastrointestinal functions.
Does Muscle burn Fat – Final Say
Evidently, building muscles helps burn fats, but not as significant as most people think. Also, we can increase our metabolic rate by engaging heavy resistance training such as weightlifting. Performing weightlifting only increases fat burning, as well as the resting metabolic rate for some hours.
Nevertheless, it is worth noting that anaerobic routine is more advisable if you intend to lose fat and replace it with muscle. Rather than performing aerobic routines such as swimming, running, jogging, among others, you should do more of anaerobic exercise such as lifting free weights. Thus, endeavour to determine what exactly are your fitness goals before hitting the gym.
Before we conclude, you are best advised not to engage weightlifting without having a guide or an instructor. Endeavor to consult a specialist who can help you draft a proper workout regime that will improve your strength, increase your metabolism, as well as reduce your body fat. Adhere to proper procedures and take necessary precautions during the workout routine. And most importantly, consistency is vital towards achieving body fitness that you have always wanted.
Other Articles you may like.
Hamstrings and Calves Stretch
Often hamstrings and calves can become tight as a result of poor posture, always sitting down as a result of our inactivity sedentary lifestyle. This lifestyle shortens the gip flexor muscles cause the hamstrings to tighten.
Abdominal Ball Crunch with Twist
The Abdominal Ball Crunch with Twist requires controls and strength to undertake. The ball provides lots of lateral movement that requires the core intelligence to work. This exercise helps tone the tummy muscles as well as strengthening your spinal muscles that will...
Ab Hip Raise
The Abdominal Hip Raise, Ab Hip Raise, or often referred to as “The Bridge” is designed to strengthening the core abdominal muscles and Quads. These muscles support the lower back, spine and help with your posture. Find out more.





